
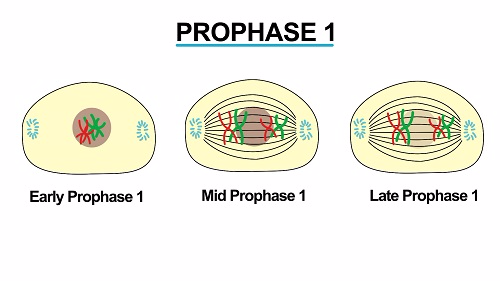
This law states that traits are inherited independently of each other. This is called crossing-over and is responsible for the other law of genetics, the law of independent assortment. At the end of prophase I and the beginning of metaphase I, homologous chromosomes are primed for crossing-over.īetween prophase I and metaphase I, homologous chromosomes can swap parts of themselves that house the same genes. This step does not take place in mitosis. This can be seen in the red and blue chromosomes that pair together in the diagram. Unlike in mitosis, the chromosomes pair with their homologous partner. The nuclear envelope degrades, which allows the microtubules originating from the centrioles on either side of the cell to attach to the kinetochores in the centromeres of each chromosome.
Prophase I, the first step in meiosis I, is similar to prophase in mitosis in that the chromosomes condense and move towards the middle of the cell. Phases of Meiosis I Meiosis Stages Prophase I They are connected at the centromere for storage but can separate into individual chromosomes. Each one of these “X” chromosomes consists of two sister chromatids – cloned DNA from replication. In the diagram below, the red chromosomes are the ones inherited from the mother, the blue from the father.Īt the start of the following diagram, the DNA has already been replicated, which is why the red and blue chromosomes look like the letter “X”.
#Prophase in meiosis full#
This means there are 4 copies of each gene, present in 2 full sets of DNA, each set having 2 alleles. Remember, before meiosis starts the normally diploid DNA has been duplicated. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. In the next division, which immediately follows the first, the two alleles of each gene are separated into individual cells. In the first division, which consists of different phases, the duplicated DNA is separated into daughter cells. Meiosis then consists of two cell divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Phases of Meiosisīefore meiosis, the DNA is replicated, as in mitosis. Meiosis occurs in two distinct divisions, with different phases in each. However, if the organism cannot survive if they are polyploidy, meiosis must occur before reproduction. In other organisms, polyploidy is common and they can exist with many copies of the same gene.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
